Areas Of The Brain
Where did you experience an injury?
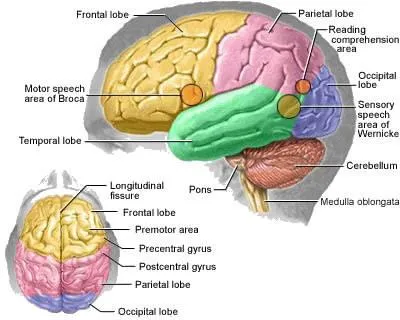
Frontal Lobe: The frontal lobe is responsible for voluntary motor functions for motor planning, expressive language, motivation, behavior, problem solving, social and initiation.
Temporal Lobe: Hearing, smell, learning, memory, visual recognition, and emotional behavior.
Broca's Area: Motor initiation/production of spoken verbal language- generates a motor program for the muscles of the larynx, tongue, cheeks, and lips to produce speech.
Parietal Lobe: Sensory reception, taste, hearing, reception of sight, touch, and smell.
Wernicke's Area: Recognition of spoken verbal language and understanding of written language (letters/numbers/etc.)
Occipital Lobe: Main visual center of brain, spatial relationships, visual perception and interpretation of color, form, and motion interpretation.
Pons: Sends signals from the cerebrum to the cerebellum and nuclei for sleep, hearing, equilibrium, taste, eye movements. fascial expressions, fascial sensation, respiration, swallowing, bladder control, and posture.
Cerebellum: Involved in voluntary motor movement, balance, equilibrium/balance, and muscle tone.
Medulla Oblongata: Receives input from the taste buds, pharynx, and input from organs. It controls the cardiac center for rate and force of heartbeat, blood pressure, and control the rate and depth of breathing.
Brain Stem: Vital part associated with control of the brain, heart, and lung. Responsible for attention, arousal, and consciousness.
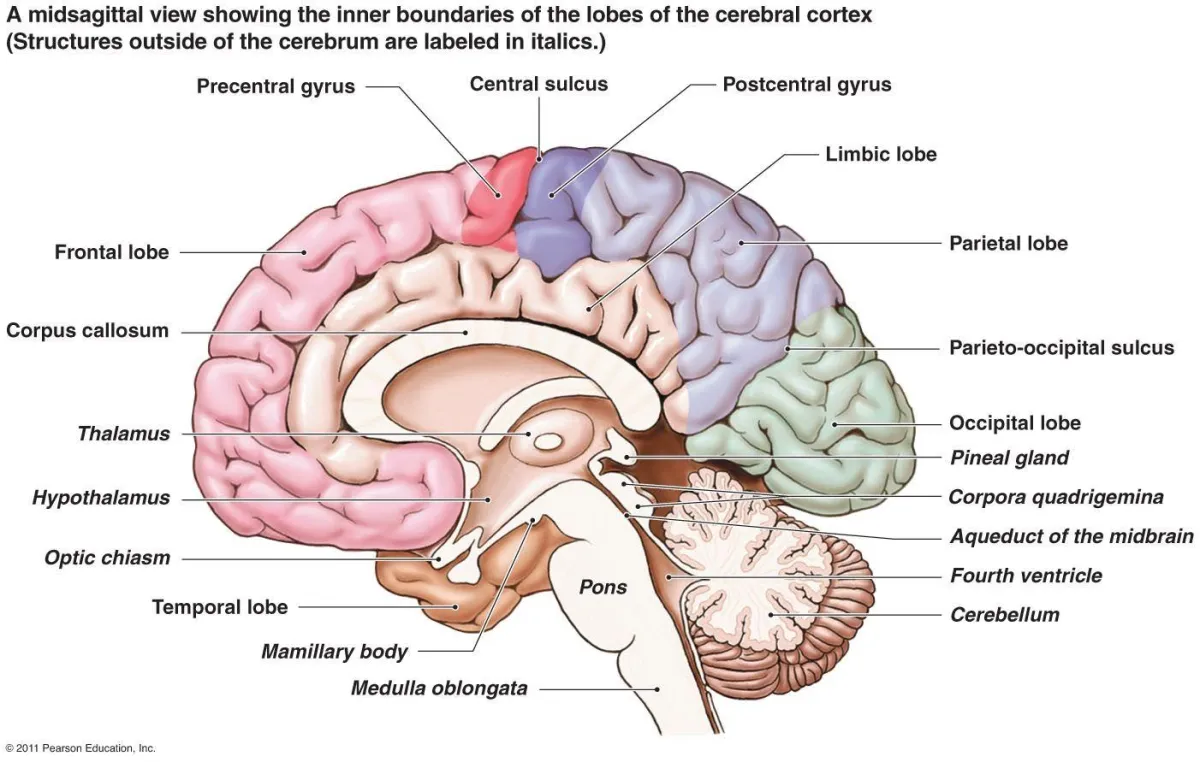
Corpus Callosum: The bridge between the left and the right hemispheres of the brain to send complex signals back and forth.
Thalamus: It is the gateway to the cerebral cortex of all sensory and motor information to the cerebral cortex. Also assists in arousal, eye movements, and other sensory input.
Hypothalamus: Control centers of sleep- wake cycle, arousal, blood pressure, sex drive, hunger, body temperature.
Optic Chiasm: It sends signals from both sides of the eyes and visual information from both sides of the brain. Receives visual signals from the visual fields of both eyes with assisting with binocular vision and eye-hand coordination.
Cerebellum: Maintains muscle tone and posture, coordinates eye and body movements, and aids in learning motor skills. It also smooths muscle movements while moving arms/legs, walking without any uncontrolled movements.
Limbic Lobe: It includes nucei in the lobe called amygdala and hippocampus. It is thought to be involved in emotion and smell with memory processing and storing.
