Different Types of Strokes
Cerebrovascular Accident
What kind did you have?
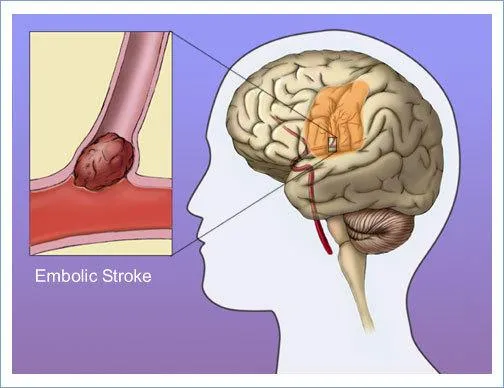
Embolic Stoke: is where a section of material, typically a blood clot from an area of the body gets dislodged and travels through the bloodstream. The clot can get lodged into a blood vessel supplying the direct bloodflow to the brain and starve the blood from reaching the brain.
An emboli can come from any area with an example would be from the heart from an irregular rhythm.
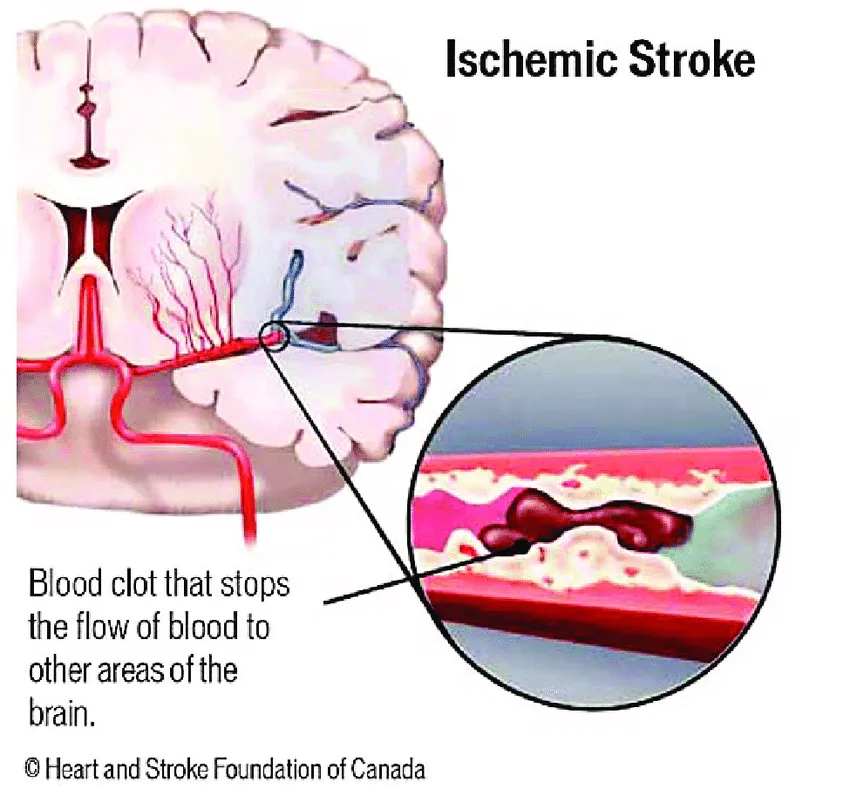
Ischemic/Thrombotic Stroke: is a blood clot formed directly on the blood vessel wall where artherosclerotic plaque causing the blood vessel to restrict the blood flow. Which is a slow clot forming in the certain blood vessel slowly restricting the brain from receiving it's important nutrients. Higher levels of cholesterol can increase your risk for an ischemic stroke.
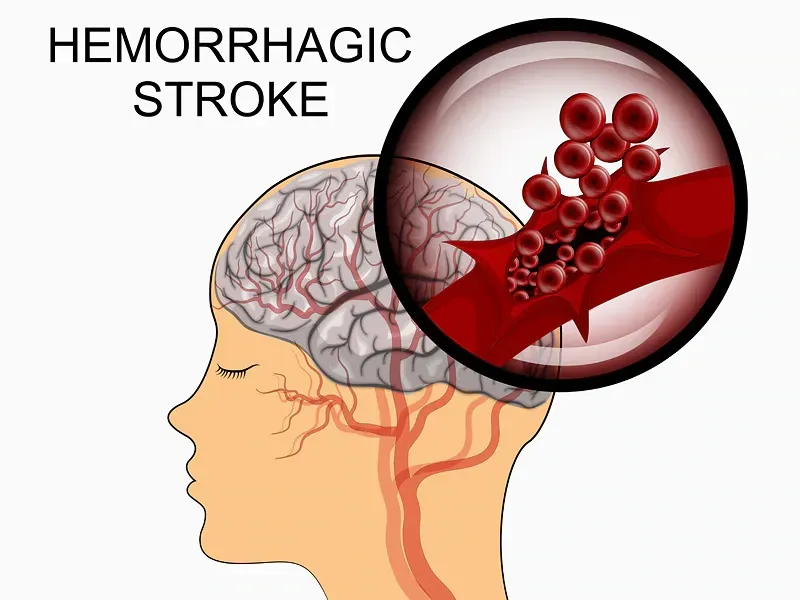
Hemorrhagic Stroke: results from a pressure involved inside the blood vessel tissue that swells and eventually ruptures reducing the blood supply to the supplied brain tissue. The pooling of the blood in the certain areas causes pressure inside the brain and swelling in the tissue. High blood pressure is usually a factor with this type of stroke.
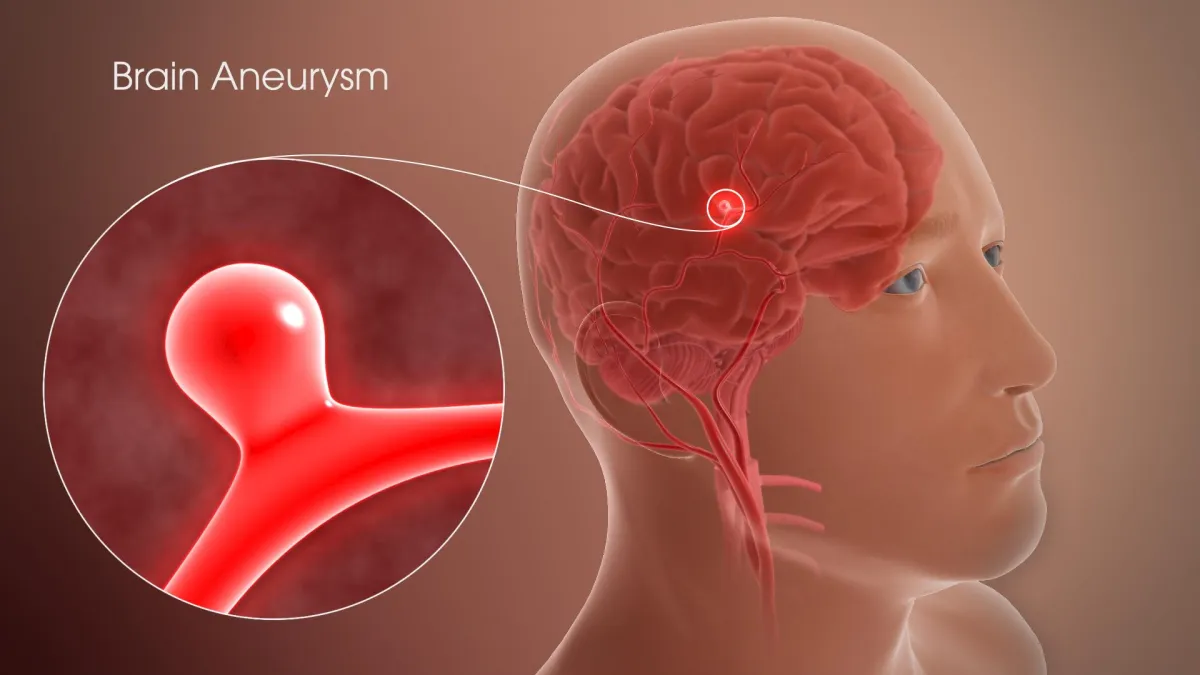
Brain Aneurysm: arise from blood vessels usually surrounding the circle of Willis in the brain looking like a ballooning or berry like shape in the weakened arterial wall. It is similar to a hemorrhagic stroke with rupturing or leaking in the blood vessel and restricting the blood supply.
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) or a mini stroke: caused by a spasm or an occlusion of an artery which causes neurological deficits which could last hours or just minutes which could be followed by a complete recovery of function. TIA's can keep reoccurring for months or years which these are warning signs of a full complete stroke is imminent. The primary cause of TIA's are mostly embolic from artherosclerotic plaque forming in a blood vessel.
